Initiatives to Address Climate Change
Sumitomo Warehouse and Group companies are engaged in a variety of initiatives aimed at reducing environmental impact and preserving the environment based on the awareness that addressing climate change is one of the most important tasks for business.
Acquisition of the CASBEE Certification
CASBEE is a tool developed by the Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation for comprehensively assessing the environmental performance of buildings.
The Company has obtained Comprehensive Assessment System for Built Environment Efficiency (CASBEE) for the following facilities as one of its initiatives to reduce environmental impact in logistics facilities and real estate leasing facilities.
Facilities that have obtained CASBEE assessment
| Name of facilities | Rating |
|---|---|
| Urayasu Warehouse | “CASBEE” Class A |
| Minami Honmoku Warehouse | “CASBEE-Yokohama” Class A |
| Nanko East Warehouse | “CASBEE-Osaka” Class A |
| Hanyu Archives No.2 | “CASBEE-Saitama” Class A |
| Nanko North Warehouse | “CASBEE-Osaka” Class A |
| Inuyama Archives | “CASBEE-Aichi” Class A |
| Yodoyabashi Mid-Cube | “CASBEE-Osaka” Class A |
| T-FRONTE | “CASBEE-Saitama” Class A |
| Chuo Logistics Center | “CASBEE-Kobe” Class A |
| Hommachi Garden City Terrace | “CASBEE-Osaka Mirai” Class A |
Initiatives Aimed at Energy Saving
Response to energy saving methods
The Company is a “specified business operator” as defined under the Act on the Rationalization etc. of Energy Use (Energy Saving Act). As a specified business operator, the Company is required to reduce the energy consumption units in its facilities by an average of 1% per year in the medium to long term and submit the results thereof to the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry as a “regular report” every year.
For this reason, the Environmental Subcommittee, which is an organization under Sustainability Committee, operates an Energy Saving Promotion Meeting, formulates energy-saving plans, tracks companywide energy usage and raises awareness concerning energy saving as initiatives to preserve the environment.
Photovoltaic system
Nanko East Warehouse, Nanko, Osaka
A photovoltaic system has been installed on the roof of the Nanko East Warehouse in Nanko, Osaka, and these generate electric power using solar energy.
About 300,000 kWh of electricity is expected to be generated annually, covering 10% of the electric power consumed by the warehouse. This amount, when converted into CO2, is equivalent to a reduction of about 96.6 tons per year, which is a contribution equivalent to that made by a forest of 56.8 hectares.
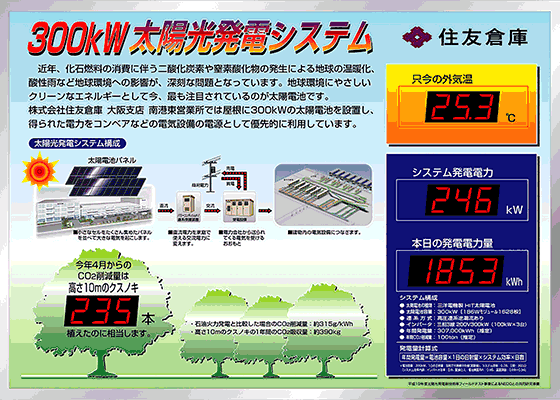
■ Outline of the photovoltaic system at Nanko East Warehouse
| Per panel | 1.44 m×0.81 m |
|---|---|
| The number of panels | 1,628 panels |
| Total area | About 1,900 m2 |
| Total weight | About 22,800 kg |
| Generation capacity | 300 kW |
Use of on-site photovoltaic services
On-site photovoltaic services are used in some warehouses located within Osaka City.
This involves renting out the Company’s warehouse rooftop space to photovoltaic business operators and using the electric power generated by the photovoltaic facilities installed by the business operator there. CO2 emissions are reduced by replacing some of the energy used in the facilities with renewable energy.
Overseas initiatives
Sumitomo Warehouse (Singapore) Pte Ltd and Sumitomo Warehouse (China) Ltd. have installed photovoltaic facilities on warehouse rooftops to provide some of the power used in these warehouses.
The installation of the facilities at Sumitomo Warehouse (Singapore) Pte Ltd was financed using Green Bonds.
Promotion of project to reduce power usage
The Company updates the air conditioning and lighting equipment used in its facilities to power-saving models as needed in an effort to reduce environmental impact and costs.
The following air conditioning update and the conversion of lighting to LEDs were financed using Green Bonds.
Air conditioning update
From 2019 to 2021, approximately 1,400 air conditioners in approximately 40 warehouses and leased buildings, etc. owned by the Company will be updated to energy-saving models.
This will reduce power consumption and CO2 emissions by approximately 30%, and is also expected to have the effect of improving the environment by using refrigerant that does not affect the ozone layer.
Conversion of lighting equipment to LEDs
From 2017 to 2019, approximately 54,000 lighting fixtures in approximately 60 warehouses, etc. owned by the Company were updated to use LED lighting. As a result, power usage and CO2 emissions were reduced by 63.8%, exceeding the initial projection of approximately 60%.
Initiative to alleviate the heat island effect using green roof
At Nanko East Warehouse in Osaka, 1,400 m2 of the building's roof space and 2,850 m2 of the surrounding ground surface have been vegetated to curb temperature increases on the roof and ground surface and mitigate the heat island effect. There is a difference of two to three degrees centigrade in the inside surface temperature between the vegetated and non-vegetated roofs, indicating that the green roof contributes to maintaining a constant temperature inside the warehouse, in addition to contributing to curbing energy consumption by reducing the operation of air conditioning.


Certification/Award History, etc.
- Japan Association for Logistics and Transport 22nd Logistics Environment Awards Special Award (Reducing CO2 emissions by switching to LED lighting, updating air conditioning equipment, and installing solar power generation equipment, and raising environmental awareness by issuing green bonds)
Initiatives to Reduce the Environmental Impact of Services
The Group would like to contribute to customers’ environmental measures by providing services with low environmental impact. At each of the Group’s business sites, an effort is made to reduce energy usage and CO2 emissions by introducing equipment with a low environmental impact when replacing warehouse facilities and cargo handling equipment, and promoting the improvement of efficiency of work and transportation.
Improvement of logistics efficiency by consolidating locations (Certification of “Comprehensive Efficiency Plan” under the Act on Advancement of Integration and Streamlining of Distribution Business)
The Company has locations that have received certification of the Comprehensive Efficiency Plan under the Act on Advancement of Integration and Streamlining of Distribution Business. The following business sites have received certification for shortening transportation distances and reducing CO2 emissions by consolidating products handled in multiple warehouses into a new facility.
Furthermore, the “modal shift” and “sharing of transportation and delivery” conducted by two or more business operators are also included in the businesses covered by the Act due to a revision in May 2016, and the domestic transportation of the feed additive methionine by ship jointly implemented with Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. and Shikoku Kaihatsu Ferry Co. Ltd. received a "Comprehensive Efficiency Plan" certification in April 2019.
| Launch | Name of sites |
|---|---|
| August, 2007 | Yokohama Branch Honmoku Logistics Center (Current: Yokohama Branch Minami Honmoku Logistics Center No.1) |
| April, 2008 | Osaka Branch Nanko East Logistics Center |
| April, 2015 | Osaka Branch Nanko North Logistics Center |
| June, 2019 | Yokohama Branch Minami Honmoku Logistics Center No.2 |
Modal shift
A modal shift is to change freight transport systems from highway truck transportation to marine and railway transportation with the aim of reducing CO2 emissions. This is an effective means of reducing CO2 emissions and also solves the problem of the truck driver shortage that has been an issue in Japan in recent years. Furthermore, in Europe and North America where land transportation distances are long, transportation using barges and railways, etc. is proposed as an alternative to transportation on highways, increasing options for customers to reduce environmental impact.
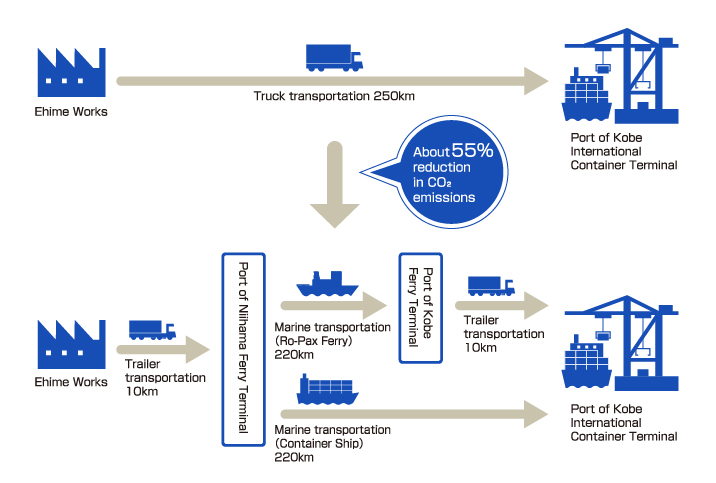
Freight transportation using shipping (Domestic vessels)
The example shown here is a customer using marine transportation to transport freight between Niihama City in Ehime Prefecture and Port of Kobe. It has helped achieve about 55% reduction in CO2 emissions compared with transportation by trucks alone.
Empty container transportation using shipping (Domestic vessels)
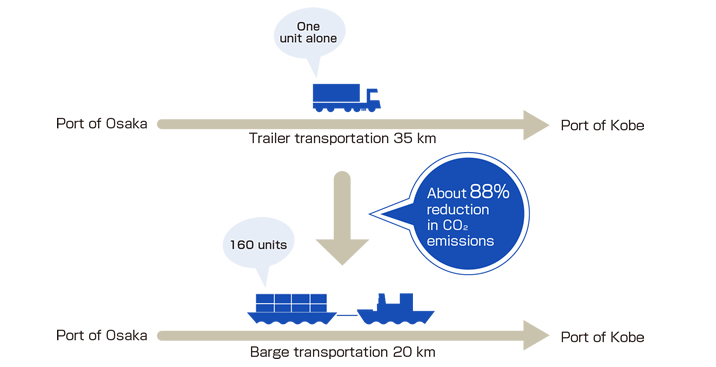
Many of the containers loaded with freight when importing and exporting are owned by shipping companies and container lease companies. An empty container is leased at the container terminal when exporting goods, and an empty container with the goods unloaded is returned to the container terminal when importing goods. The balance of container supply and demand is often not constant at container terminals, and it is necessary to bring empty containers from another terminal when there is a shortage for lending them, and the long distance of such land transportation has become an issue.
To address this, customers managing containers are presented with the proposal to transport empty containers from terminals with a surplus to terminals with a shortage by marine transportation using barges instead of land transportation.
The figure shows an example of transportation of empty containers between the Port of Osaka and the Port of Kobe. In this case, CO2 emissions can be reduced by approximately 88% compared to trailer transportation.
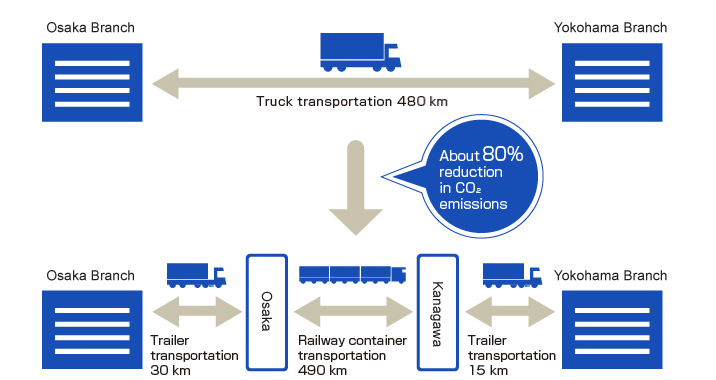
Freight transportation using railway
We use a rail service to transport freight between the distribution centers operated in Kanagawa Prefecture and in Osaka City, respectively. Transportation by railway has helped achieve about 80% reduction in CO2 emissions compared with transportation by trucks alone.
Initiatives Aimed at Round-trip Use of Containers
Customers importing and exporting goods are presented with a proposal for round-trip use to reduce transportation related to the return and leasing of empty containers by using empty containers that have been unloaded after importing to be reused as containers for exporting goods. Like the modal shift, this round-trip use of containers reduces CO2 emissions and can also lead to solving the problem of the driver shortage.
Provision of Low-Carbon Logistics Services in Air Cargo Transportation
To achieve carbon neutrality, we offer an environmentally friendly air cargo transportation service that utilizes the environmental value of SAF (Sustainable Aviation Fuel), which is expected to be a next-generation aviation fuel, in our role as a freight forwarder.
Certification/Award History, etc.
- Feed Additive Methionine Logistics Operations Certified by Government as "Comprehensive Efficiency Plan"
- Japan Association for Logistics and Transport 23rd Logistics Environment Awards Special Award (Initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions by changing the port of discharge)
- Japan Association for Logistics and Transport 22nd Logistics Environment Awards Special Award (Initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions through container round use)
Initiatives to Reduce Energy Usage and CO2 Emissions
Based on the awareness that measures to address climate change are one of the important issues in our business, the Group has set a target of reducing greenhouse gas emissions of Scopes 1 and 2 on a non-consolidated basis by 50% from the FY2018 level by FY2030 and is conducting initiatives to achieve this target.
Warehouse facilities
- The Group is promoting the introduction of electric cargo handling equipment.
- Energy usage is being reduced by systematically switching to LED lighting and highly efficient air conditioning facilities.
- Photovoltaic facilities have been installed in some warehouses to provide some of the electric power used, and the use of electricity derived from renewable energy is being expanded by using on-site photovoltaic services and purchasing from electric power companies.
- The use of electric vehicles (EVs) for company cars (passenger cars mainly used for traveling between sales offices, etc.) is being promoted.
Ports and harbors (Container terminals and local piers)
- Hybrid cargo handling equipment has been introduced to reduce CO2 emissions.
- A decision has been made to introduce hydrogen fuel cell retrofitted and electric-powered RTGs (Rubber Tired Gantry cranes).
- 100% use of electricity derived from renewable energy has been achieved at the container terminals we operate in Tokyo and Yokohama ports.
Leased buildings, etc.
- Reduction of tenant energy usage and reduction of costs have been achieved by systematically switching to LED lighting and highly efficient air conditioning facilities.
- We are switching to electricity derived from renewable energy for rental real estate buildings.
- The Building Energy Management System (BEMS)* has been introduced at Yodoyabashi Mid-Cube.
※A management system for energy saving and optimizing operations in buildings such as office buildings and factories by comprehensively monitoring and automatically controlling the entire building’s energy facilities. This enables the building’s energy usage to be tracked and appropriately managed.
Participation on Projects Contributing to the Environment
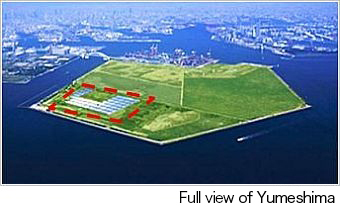
The Company has participated in the mega-solar project called “Osaka Hikarinomori Project” since October 2013 as part of its CSR initiatives.
Osaka City, Sumitomo Corporation, Sumitomo Mitsui Finance and Leasing Co., Ltd., and Summit Energy Corporation jointly implement this large-scale (10 MW) photovoltaic power generation (mega-solar) project in a 15-hectare area within the landfill disposal site on Yumeshima provided free of charge by Osaka City.
Through the project, the Company aims to contribute to global environmental conservation by promoting renewable energy, and to regional revitalization by supporting effective land use.
Outline of the mega-solar project
| Location | Location Approx.15-hectare area within the landfill disposal site on Yumeshima(Area 1), Konohana-ku, Osaka |
|---|---|
| Period | 20 years from October 2013 |
| Power generation capacity | 500 kW (apportioned according to the investment amount of Sumitomo Warehouse; equivalent to the power used by 160 typical households) |